Indian Railways, serving over 8 billion passengers annually, faces persistent challenges in service delivery that generate thousands of complaints daily.
Based on comprehensive research and analysis of official data, passenger feedback, and railway statistics for FY25, here are the most prominent complaint categories that dominate grievance submissions through RailMadad and other channels.
1. Ticketing and Reservation Issues
The most critical area of passenger frustration involves the booking and reservation process. IRCTC platform outages have become increasingly frequent, with passengers reporting system failures during peak booking hours, especially for Tatkal tickets. The advance reservation period was reduced from 120 to 60 days in 2024 to address a 21% cancellation rate and reduce fraudulent bookings. Technical glitches, waitlist confusion, and chart preparation delays continue to disrupt travel plans, with passengers often unable to confirm their journey status until the last moment.
2. Overcrowding and Unauthorized Passenger Issues
Reserved compartments being occupied by ticketless passengers has emerged as a major safety and comfort concern. Confirmed ticket holders frequently find their allocated seats occupied by unauthorized travelers, creating chaotic conditions particularly in sleeper and AC coaches. The recent New Delhi railway station stampede that killed 18 passengers highlighted the severity of overcrowding issues. Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw has directed officials to identify busy routes and introduce special trains, but the problem persists during peak travel periods.
3. Cleanliness an a chronic issue despite various cleanliness initiatives.
Passengers consistently report dirty toilets, unclean coaches, and poor waste management across the network. The Clean My Coach service, accessible via SMS to 58888, was introduced to address real-time cleaning requests, but implementation varies across routes. Station cleanliness contracts are often inadequately managed, with some stations lacking basic housekeeping arrangements.
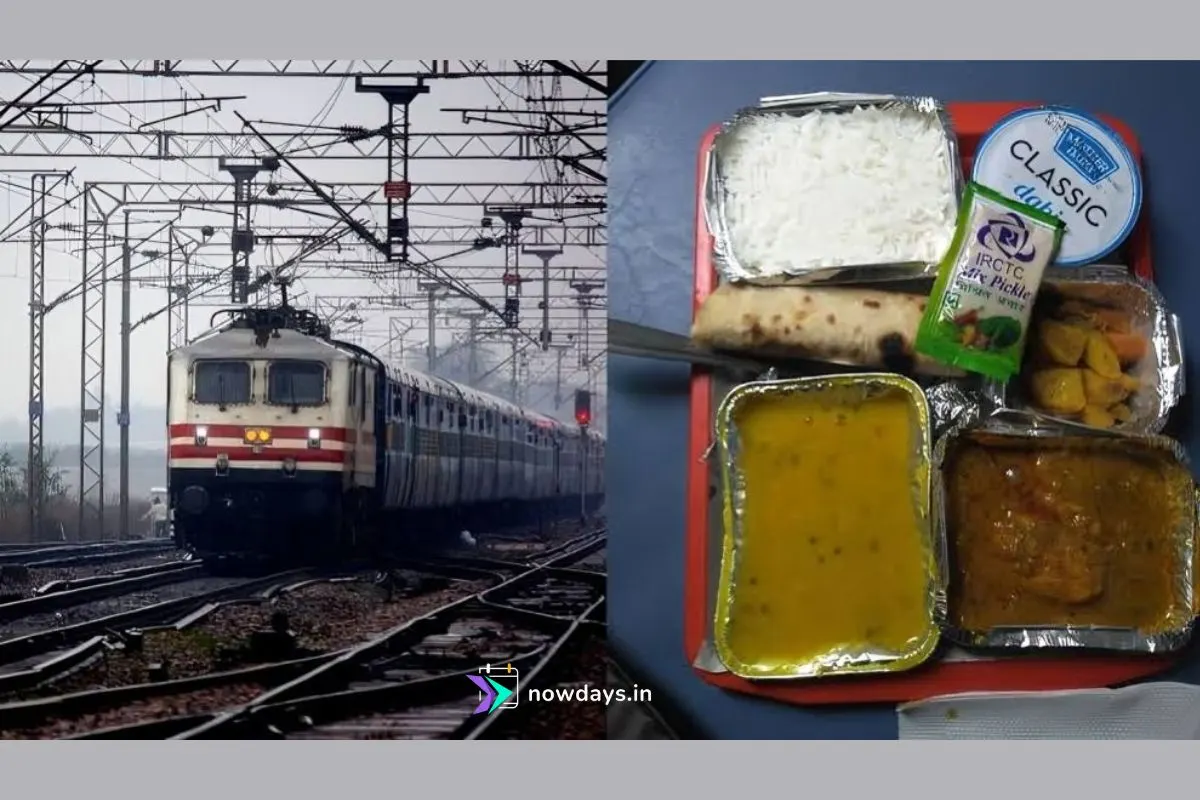
4. Food Quality and Overcharging
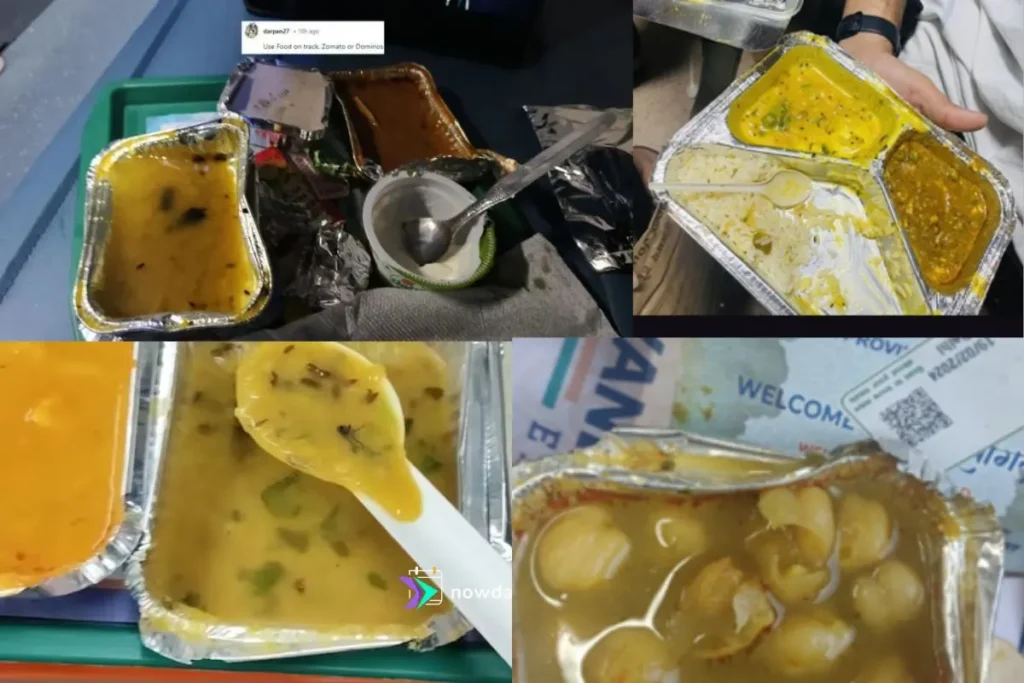

Catering services attract significant criticism, with Indian Railways receiving over 19,000 complaints about poor food quality in the past five years. FY25 alone saw 6,645 food-related complaints, with issues ranging from stale meals to overcharging for basic items. Pantry staff misconduct, including violence against passengers who complain about pricing, has been documented. The IRCTC has implemented various measures including menu stickers and toll-free complaint numbers, but enforcement remains inconsistent.
5. Infrastructure and Amenities Failures
Non-functional onboard facilities significantly impact passenger experience. Air conditioning failures, broken charging points, malfunctioning lights, and poor-quality bedding are frequently reported issues. The Railway Development Organisation (RDSO) has identified basic amenity failures as a major challenge affecting passenger satisfaction. Aging rolling stock and delayed maintenance compound these problems, particularly on long-distance routes.
6. Train Delays and Punctuality
Punctuality has shown alarming decline, with Mail/Express train punctuality dropping from 79% in 2012-13 to 69.23% in 2018-19. Despite claims of improvement, with Railway Minister reporting that 49 out of 68 divisions have achieved over 80% punctuality, passengers continue to face significant delays due to infrastructure constraints, weather conditions, and operational inefficiencies. Poor communication about delay causes further aggravates passenger frustration.
7. Security and Safety Concerns

Railway security remains inadequate, with crime rates more than doubling over recent years. The absence of Railway Protection Force (RPF) personnel, unauthorized entry into compartments, and theft incidents create safety concerns, especially for women and elderly passengers. The security management system requires systematic overhaul, as highlighted by CAG reports documenting gaps in protection measures.
8. Water Supply and Availability
Water shortages in train toilets and washbasins are persistent problems, particularly on long-distance routes. Indian Railways has introduced a quick watering system to reduce filling time from 20 minutes to 5 minutes at 142 stations. However, implementation has been slow, and passengers frequently report non-functional taps and empty flush tanks. Emergency water transportation by special trains during drought periods demonstrates the severity of water supply challenges.
9. Staff Behavior and Corruption
Railway employees topped India’s corruption complaint list in 2023 with 10,447 cases, representing the highest among all government departments. Issues include misuse of official positions, bribery, harassment of passengers, and poor customer service attitudes. The Railway Board has initiated termination procedures for convicted officers, but systemic problems persist across the network.
10. Customer Service and Grievance Redressal
Despite the introduction of RailMadad and the integrated helpline 139, complaint resolution remains unsatisfactory. Passengers report slow responses, inadequate follow-up, and unhelpful customer service representatives. While the system processes over 3,000 grievances daily with claimed 94% resolution within 2-3 hours, passenger feedback suggests significant gaps between reported metrics and actual service experience.
Addressing the Challenges: Railways’ Response
Indian Railways has implemented several technological solutions including RailMadad for complaint tracking, integrated helpline systems, and improved vendor monitoring mechanisms. The introduction of modern passenger reservation systems by December 2025 promises enhanced booking capabilities. However, the persistence of these top 10 complaint categories in FY25 indicates that structural reforms beyond technological upgrades are necessary.
Enhanced Infrastructure Investment: The government’s focus on infrastructure modernization through initiatives like the National Rail Plan and dedicated freight corridors aims to address capacity constraints and improve service quality.
Digital Integration: Advanced systems for real-time monitoring, automated complaint redressal, and passenger communication are being deployed to enhance service responsiveness.
Safety Measures: Implementation of Kavach (Automatic Train Protection System) and improved security protocols aim to address safety concerns, though deployment remains limited.
The challenge for Indian Railways lies in balancing its social obligation to provide affordable transportation with the need for quality service delivery. While technological improvements and increased investment show promise, addressing these top 10 complaint categories requires sustained effort in operational efficiency, staff training, and systematic reforms to meet passenger expectations in the world’s fourth-largest railway network.